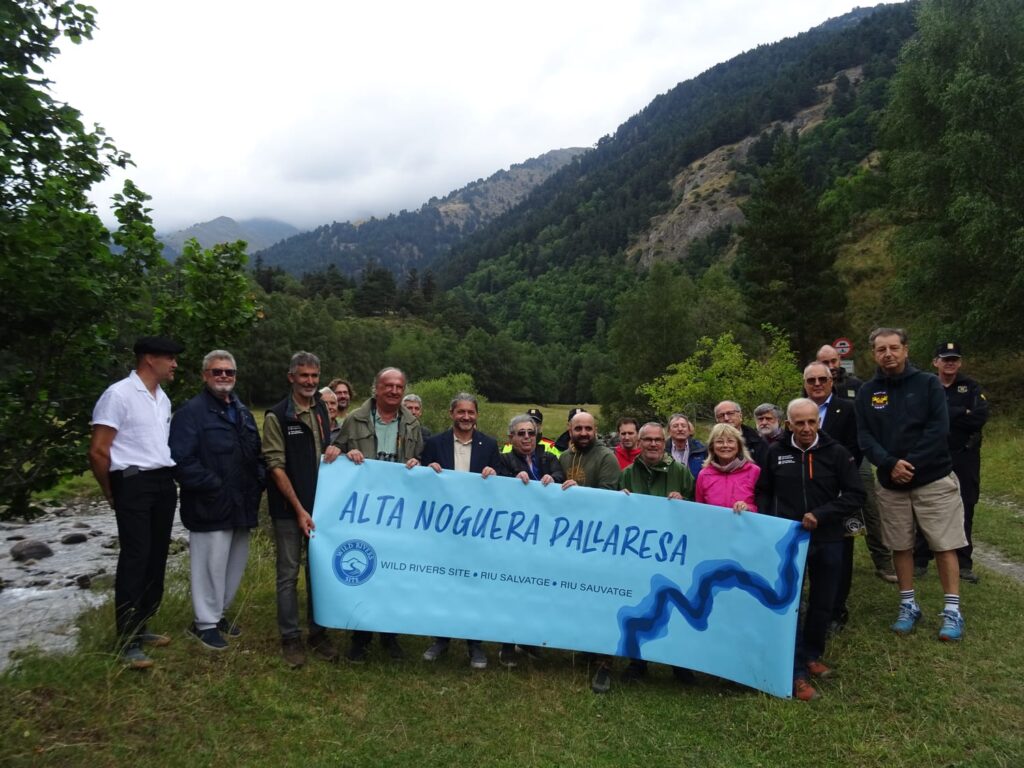
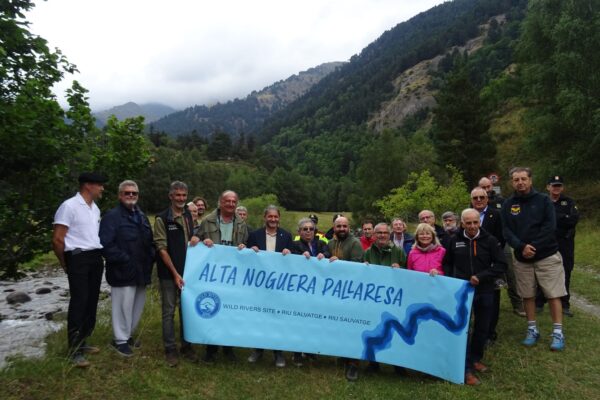
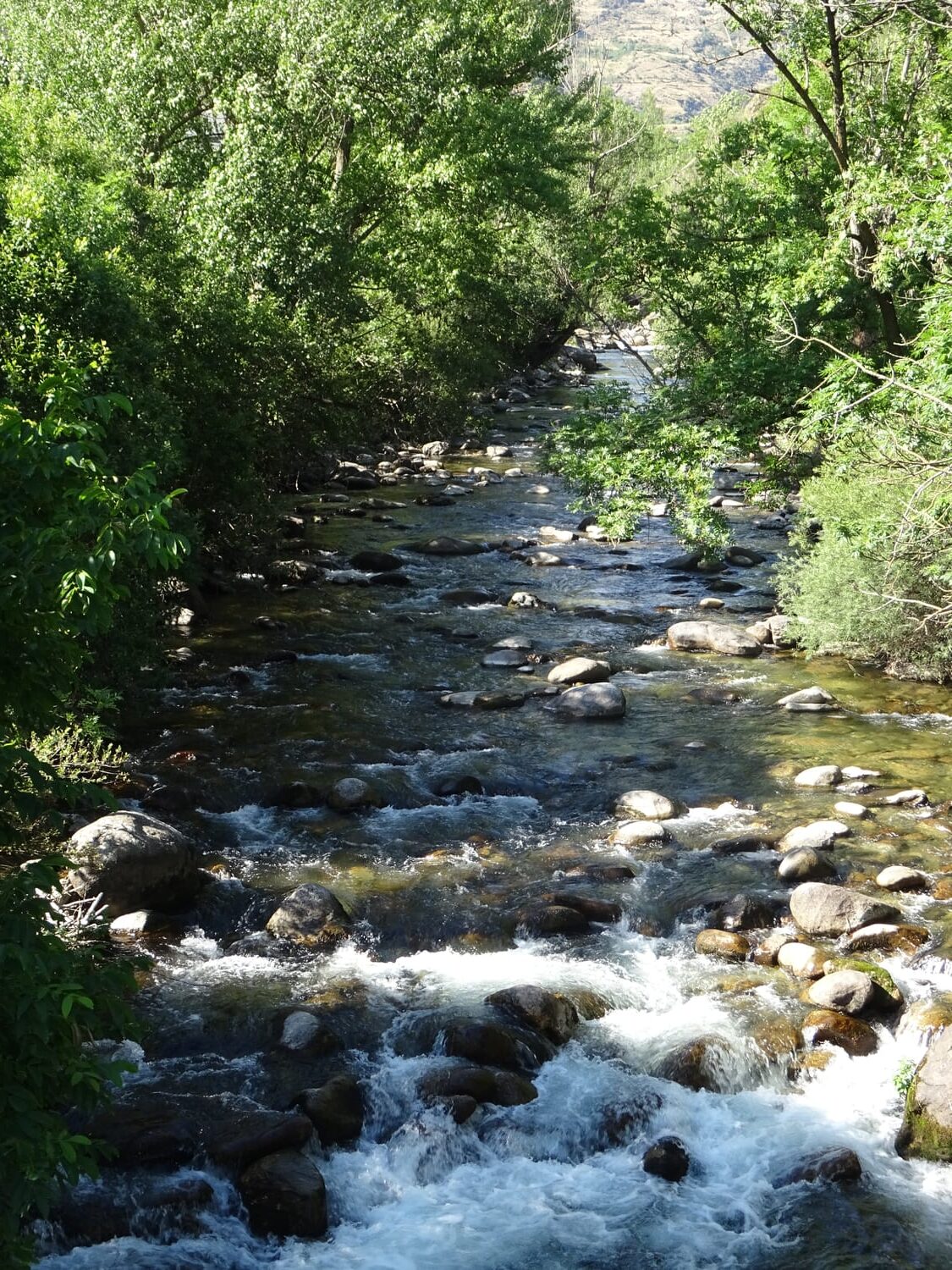
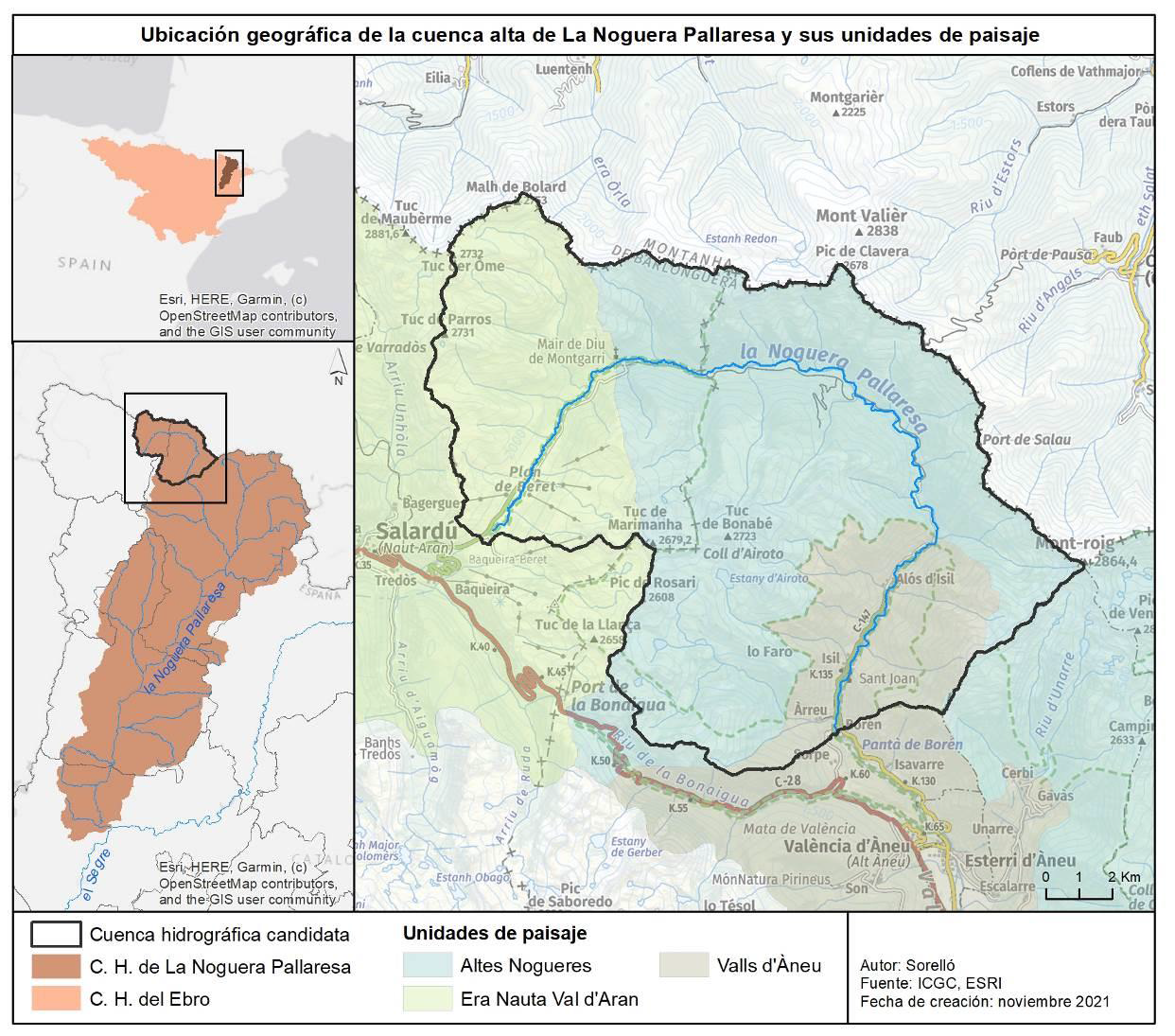
The Alta Noguera Pallaresa, located in the Spanish Pyrenees, is a tributary of the Segre River, which is itself a tributary of the Ebro. The first 10 kilometres of the river are located in the Val d’Aran department, which is responsible for ‘natural environment management’ within its territory. The next 20 kilometres are located in the Alt Pirineu Natural Park, which also has responsibility for this area. On this second section, most of the riverbank plots are municipal pastures, where livestock roam freely. In winter, access is strictly prohibited, while in summer it is mainly hikers on the famous GR11 trail who enjoy the landscape, as this trail winds along the western slope, with a refuge near the river.
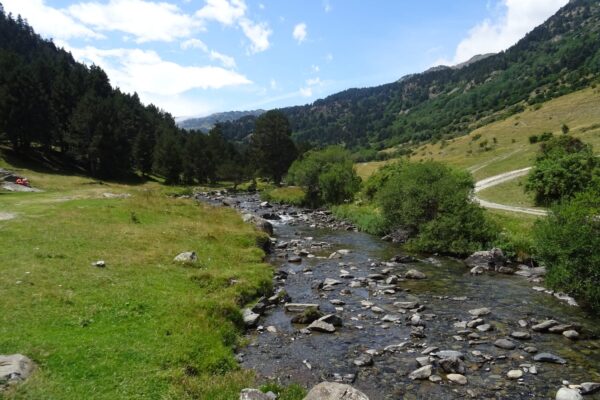
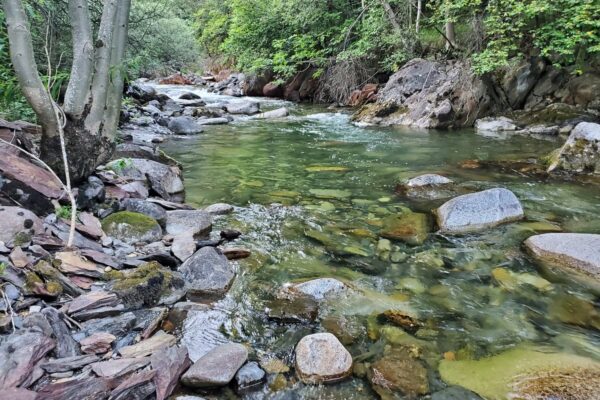
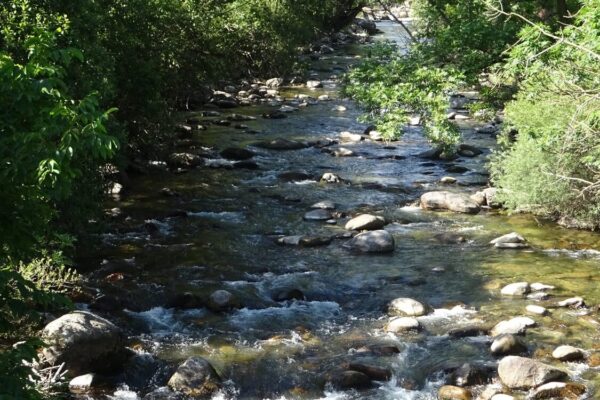
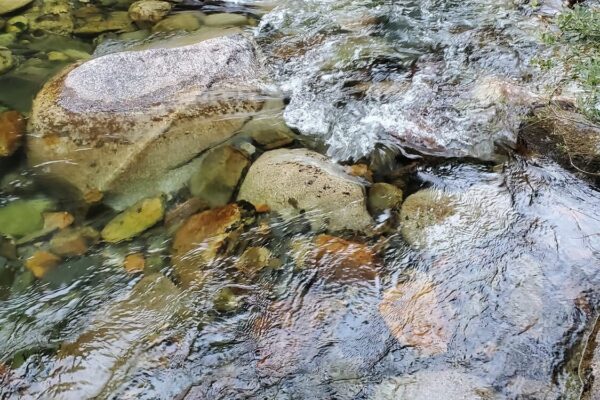
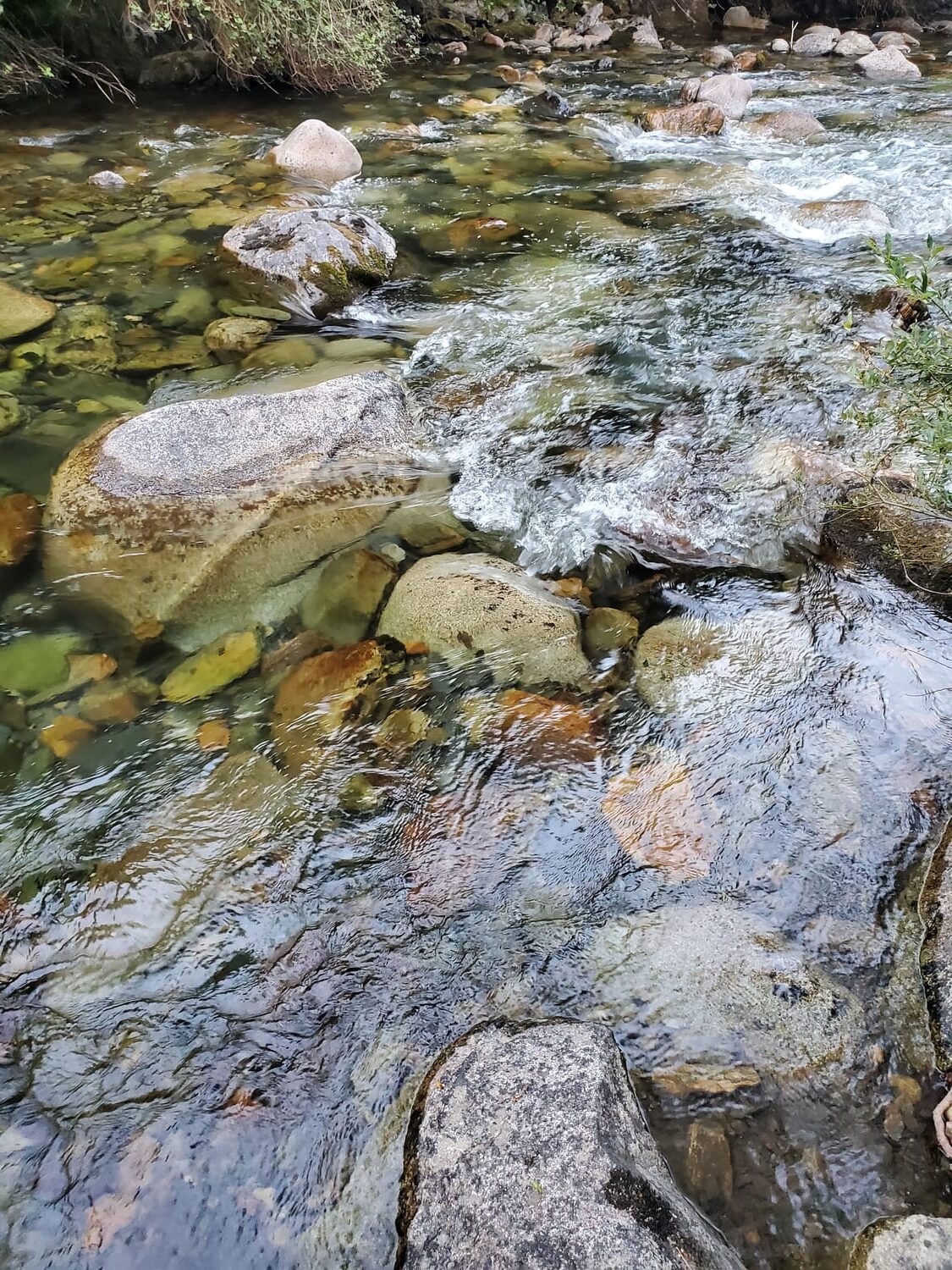
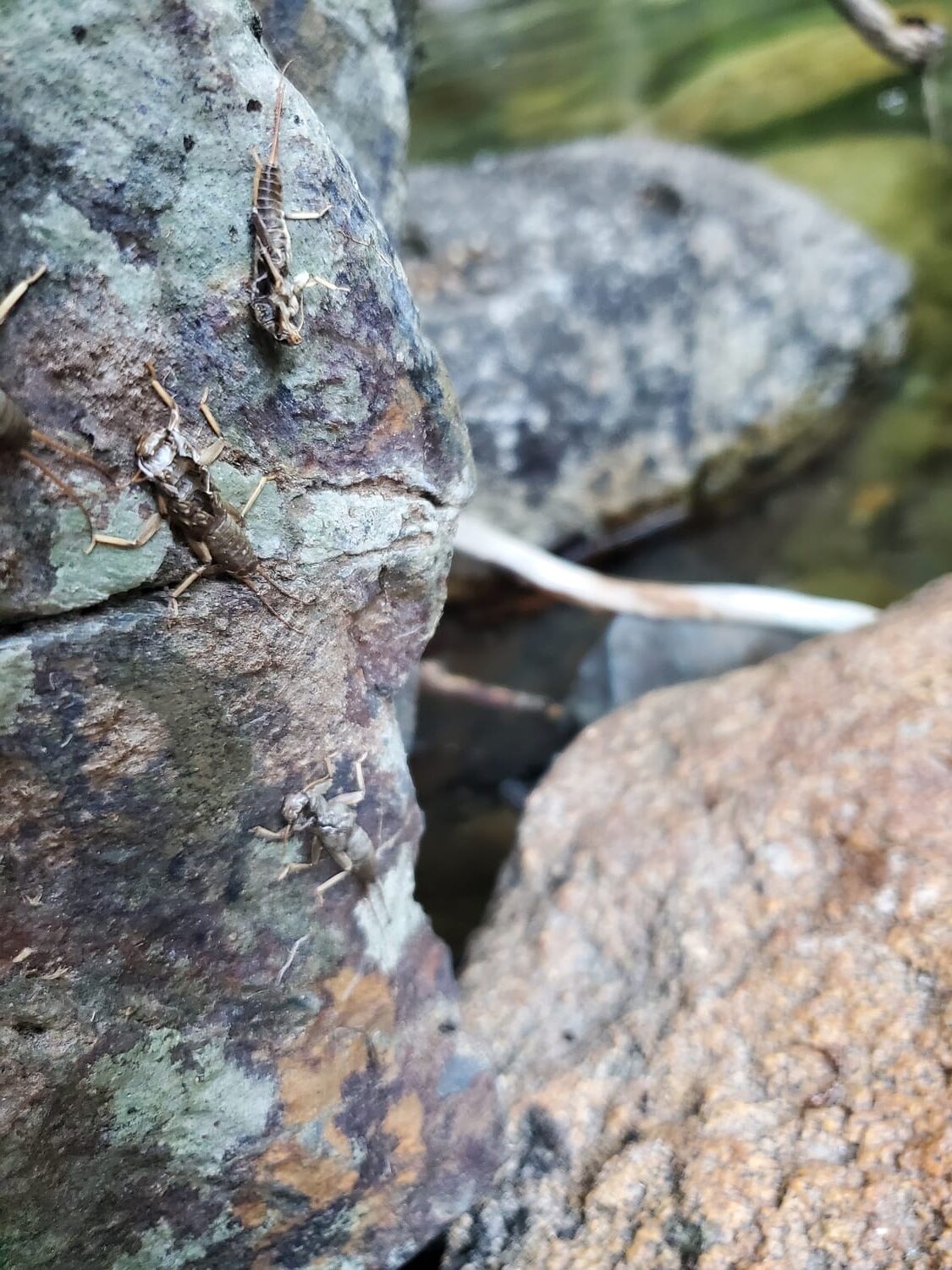
The 32.2 km stretch of the Alta Noguera Pallaresa river is in exceptional condition, with no significant alterations noted in this area, except for the presence of a ski resort located at the head of the watershed. From a fisheries perspective, the entire section is classified as a ‘genetic reserve’ by the Catalan environmental authorities, which prohibits any fish stocking, while the uppermost 22 km of the river are classified as ‘no kill’.
The natural hydrological regime of the basin is of the snow-rain type, with the heaviest rainfall occurring in autumn and spring, and particularly high flow rates during the thaw period between April and June, when the river receives the greatest amount of water. Temperatures are determined by the altitude gradient, with an average of around 4°C at the springs and 8°C at the bottom of the valley. As for precipitation, the average value for the basin is around 1,100 mm/year (with a minimum of 800 mm at an altitude of 1,200 m and a maximum of 1,250 mm at an
altitude above 2,200 m). The prevailing climate in the region is Atlantic.

















 Maison de la Culture et de la Citoyenneté
Maison de la Culture et de la Citoyenneté